Lesson Objective
- Understand what software is.
- Explain the differences between system and application software.
- Should also be able to list and describe programs from different software categories.
KS3, GCSE, A-Level Computing Resources
Software refers to a collection of programs and data that instruct a computer on how to perform specific tasks. The image below show software broken down into various categories.
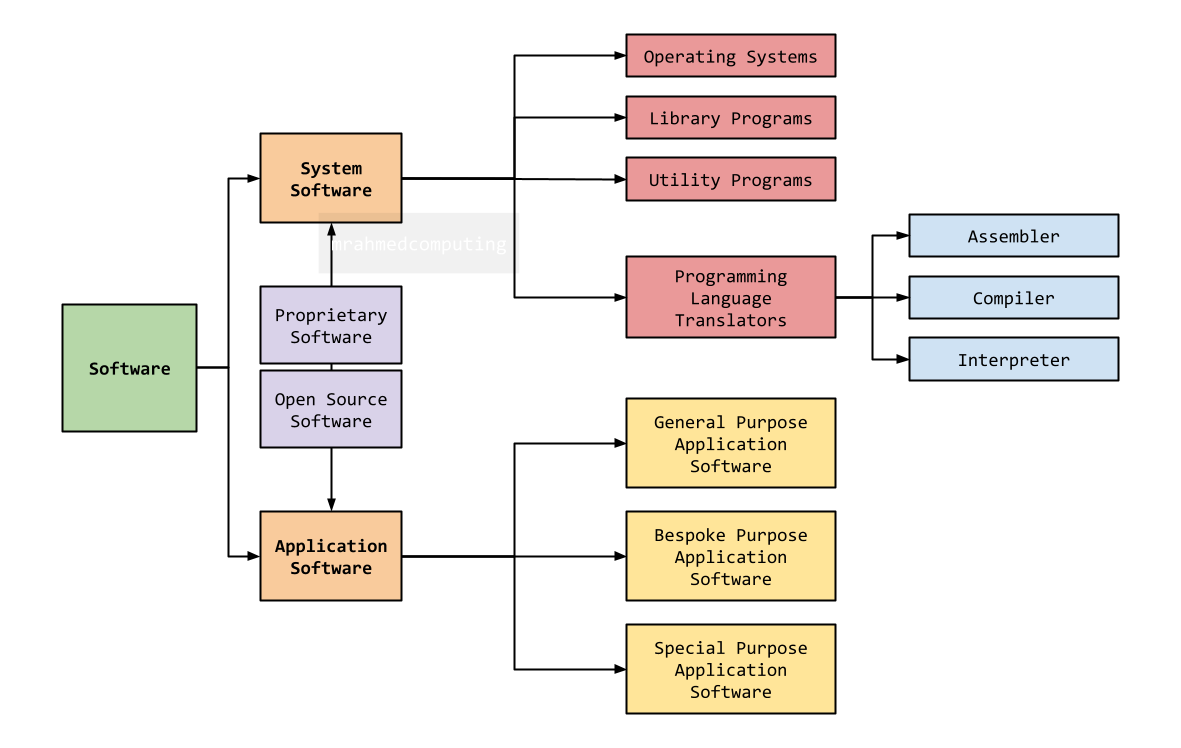
Application software, also known as app or software application, refers to a category of computer programs designed to perform specific tasks for end-users.
Application software enables users to create, edit, design, browse, communicate, and play with various applications. It can manipulate text, numbers, audio, graphics, or a combination of these elements. Examples include word processors, media players, and accounting software.
General purpose software is versatile and can be used for a variety of tasks. It is not limited to one specific function.
Examples:
Bespoke software is tailor-made for a specific user or organization. It is customized to meet precise needs.
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Examples:
Special purpose software is designed for a specific task or function. It serves a singular purpose.
Examples:
System software performs the tasks needed to operate the hardware.
System software refers to the low-level software that manages and controls a computer's hardware and provides basic services to higher-level software. It serves as the interface between the hardware and the end users, allowing users to interact with the hardware and use various applications and programs.
Here are examples of System Software:
Operating systems act as interface between user and hardware. The operating system hides the complexity of the hardware from the user. Manages hardware and runs software and also:
A library in computing refers to a collection of resources used during software development to implement computer programs. These resources can include:
Open source software is computer software whose source code is available openly on the internet. Programmers can modify it to add new features and capabilities without any cost.
Examples:
Proprietary software is copyrighted and its source code is not publicly available. Only the company that created it can modify and distribute it. They are the legal owners of the software.
Examples: