Lesson Objective
- Define what a computer network is (LAN, WAN and PAN).
- Define the term Standalone Machine.
- Give examples of different computer networks.
- Identify and explain advantages and disadvantages of computer networks.
KS3, GCSE, A-Level Computing Resources
A network is a group of computers connected together that can share data and resources. The biggest network in the world is the Internet, a collection of networks all round the world
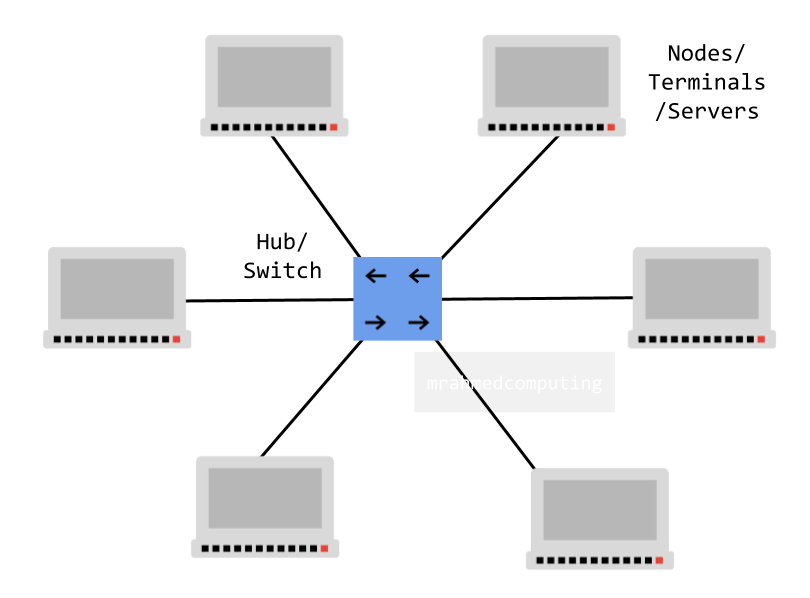
Characteristics of a LAN:
Characteristics of a WAN:

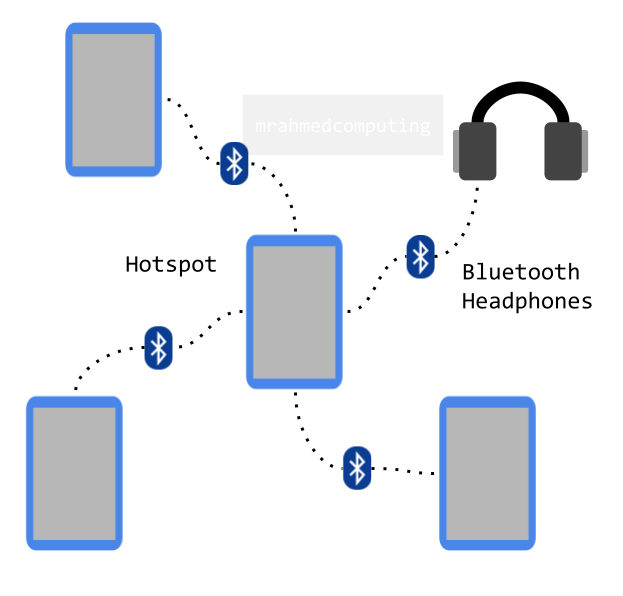
A WPAN is a group of devices connected without wires or cables. Most PANs for everyday use are wireless, using close-range wireless protocols like Bluetooth. The range of a WPAN is usually very small, typically not efficient over distances larger than 5-10 meters.
Examples: One common real-world example of a PAN is the connection between a Bluetooth earpiece and a smartphone. PANs can also connect laptops, tablets, printers, keyboards, and other computerized devices.
Hotspot? While devices within a PAN can exchange data with each other, PANs typically do not connect directly to the Internet. However, a device within a PAN can be connected to a local area network (LAN), which in turn connects to the Internet.
Extra: PAN and BAN (Body Area Network) are different. A Body Area Network (BAN) typically refers to medical sensors with wireless connectivity placed on, embedded in, or carried near the human body.